算法题
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
返回其自底向上的层次遍历为:
[ [15,7], [9,20], [3] ]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public IList<IList<int>> LevelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
IList<IList<int>> res = new List<IList<int>>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new Queue<TreeNode>();
q.Enqueue(root);
while(q.Count > 0)
{
IList<int> data = new List<int>();
int count = q.Count;//临时保存某层的数量
//一下子将这层遍历完,然后队列里的就全是下一层的了
for(int i = 0;i<count;i++)
{
TreeNode node = q.Dequeue();
if(node == null) continue;
data.Add(node.val);
q.Enqueue(node.left);//随便加进去啦
q.Enqueue(node.right);
}
if(data.Count > 0)
res.Insert(0,data);
}
return res;
}
}
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1 / \ 2 2 / \ / \ 3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1 / \ 2 2 \ \ 3 3
迭代的方式
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
//两条队列
Queue<TreeNode> left = new Queue<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> right = new Queue<TreeNode>();
left.Enqueue(root.left);
right.Enqueue(root.right);
while(left.Count > 0 && left.Count == right.Count)
{
//保证左边的结点,对上的是右边的结点
TreeNode l = left.Dequeue();
TreeNode r = right.Dequeue();
if(l == null && r == null) continue;
if(l == null || r == null) return false;
if(l.val == r.val)
{
left.Enqueue(l.left);//左边的先左后右
left.Enqueue(l.right);
right.Enqueue(r.right);//右边的先右后左
right.Enqueue(r.left);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return left.Count == right.Count;
}递归的方式:
public class Solution {
public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return IsSymmetric(root,root);
}
public bool IsSymmetric(TreeNode one,TreeNode two)
{
//前两个判断可以保证one和two都不为null
if(one == null && two == null) return true;
if(one == null || two == null) return false;
return (one.val == two.val) && IsSymmetric(one.left,two.right) && IsSymmetric(one.right,two.left);
}
}
给定两个二进制字符串,返回他们的和(用二进制表示)。
输入为非空字符串且只包含数字 1 和 0。
示例 1:
输入: a = "11", b = "1"输出: "100"
示例 2:
输入: a = "1010", b = "1011"输出: "10101"
public string AddBinary(string a, string b) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int aLen = a.Length;
int bLen = b.Length;
int up = 0;
int index = 0;
int temp = 0;
while(index < aLen || index < bLen)
{
temp = 0;
if(index < aLen)
{
temp += a[aLen - index - 1] - '0';//转化为数字0和1
}
if(index < bLen)
{
temp += b[bLen - index - 1] - '0';//转换为数字0和1
}
temp += up;//加上进位值
up = temp / 2;//是否进位
temp = temp % 2;//当前位置的值
res.Insert(0,(char)(temp + '0'));
index++;//向前推进
}
if(up > 0)
{
res.Insert(0,'1');//最后处理没处理到的进位
}
return res.ToString();
}
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]输出: 4
public int SingleNumber(int[] nums) {
int xor = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<nums.Length;i++)
{
//对同一个元素的两次异或操作等同于+1又-1那样
xor ^= nums[i];
}
return xor;
}因为是由0开始,任何数与0的异或都是等于它本身,而任何数与自己异或都是等于0的,所以数据中所有两个相同的数之间的异或都变成0了,最后那个唯一的元素和0异或操作,还是等于它本身就是结果了。
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
返回它的最小深度 2.
public int MinDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
{
return 0;
}
//根节点不能算是叶节点的情况
if(root.left == null)
{
return MinDepth(root.right) + 1;
}
if(root.right == null)
{
return MinDepth(root.left) + 1;
}
return Math.Min(MinDepth(root.left),MinDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
给定一个正整数,返回它在 Excel 表中相对应的列名称。
例如,
1 -> A 2 -> B 3 -> C ... 26 -> Z 27 -> AA 28 -> AB ...
示例 1:
输入: 1输出: "A"
示例 2:
输入: 28输出: "AB"
示例 3:
输入: 701输出: "ZY"
public string ConvertToTitle(int n) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int temp = 0;
while(n > 0)
{
temp = n % 26;
n = n / 26;
if(temp == 0)
{
//特殊的26的倍数处理
temp = 26;
n = n - 1;
}
res.Insert(0,((char)(temp+64)));
}
return res.ToString();
}
给定一个Excel表格中的列名称,返回其相应的列序号。
例如,
A -> 1 B -> 2 C -> 3 ... Z -> 26 AA -> 27 AB -> 28 ...
示例 1:
输入: "A"输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: "AB"输出: 28
示例 3:
输入: "ZY"输出: 701
public int TitleToNumber(string s) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<s.Length;i++)
{
res = res * 26 + s[i] - 'A' + 1;
}
return res;
}可以把它想象成是一个26进1的数字,但是又有点不同。
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的众数。众数是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在众数。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3] 输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2] 输出: 2
public int MajorityElement(int[] nums) {
int i = 0;//假设的众数指标
int j = 1;//进度指标
int count = 0;//计数
//计数超过一半前
while(count < (nums.Length - i)/2 && j < nums.Length)
{
if(nums[j] == nums[i])
{
count++;
}
else
{
count--;
}
if(count == -1)
{
//前面为成对不相等的值,抛弃掉,重新计数
i = j + 1;
j = i + 1;
count = 0;
}
else
{
j++;//进度向前
}
}
return nums[i];
}解析请查看主元素问题
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成杨辉三角的前 numRows 行。
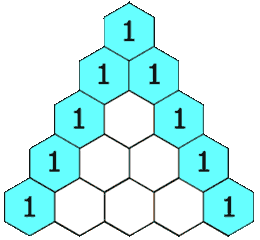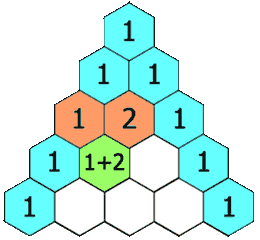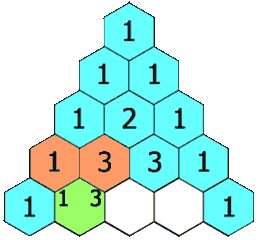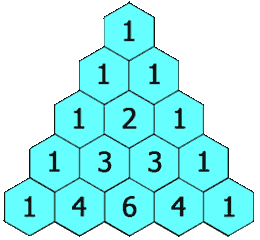
 在杨辉三角中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
在杨辉三角中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
示例:
输入: 5输出:[ [1], [1,1], [1,2,1], [1,3,3,1], [1,4,6,4,1] ]
public IList<IList<int>> Generate(int numRows) {
IList<IList<int>> datas = new List<IList<int>>();
if(numRows == 0) return datas;
IList<int> data = new List<int>();
data.Add(1);//第0行特殊化处理
datas.Add(data);
for(int i = 1;i < numRows;i++)
{
data = new List<int>();
data.Add(1);
for(int j = 1;j < i;j++)
{
data.Add(datas[i-1][j] + datas[i-1][j-1]);
}
data.Add(1);
datas.Add(data);
}
return datas;
}
给定两个二叉树,编写一个函数来检验它们是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
输入: 1 1 / \ / \ 2 3 2 3 [1,2,3], [1,2,3] 输出: true
示例 2:
输入: 1 1 / \ 2 2 [1,2], [1,null,2] 输出: false
示例 3:
输入: 1 1 / \ / \ 2 1 1 2 [1,2,1], [1,1,2] 输出: false
public bool IsSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//边界,递归到叶节点的子节点
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
//安全判断的同时也可以判断是否相同,保证p和q都不为空
if(p == null || q == null) return false;
bool left = IsSameTree(p.left,q.left);//递归对比每一个左子树
bool right = IsSameTree(p.right,q.right);//递归对比每一个右子树
//结合每一个左子树和右子树的对比结果,还有根节点的对比
return left && right && (p.val == q.val);
}
//一次过,这是我没想到的,哈哈哈。