using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class LogTEST : MonoBehaviour {
void Start () {
//在一个日志信息上注册一个委托来被调用
Application.RegisterLogCallback (MyLogCallback);
}
/// log callback check
/// </summary>
/// <param name="condition">log内容.</param>
/// <param name="stackTrace">log产生的栈数据追踪</param>
/// <param name="type">log的类型.</param>
void MyLogCallback (string condition, string stackTrace, LogType type){}
}在MyLogCallback里面会接受到所有的Debug输出的日志,我们可以在这里整合信息,保存起来,然后使用GUI显示出来,实现一个运行时的Console。也可以使用WWWForm来发送错误报告,在服务端生成多用户的日志报告,分析情况等。
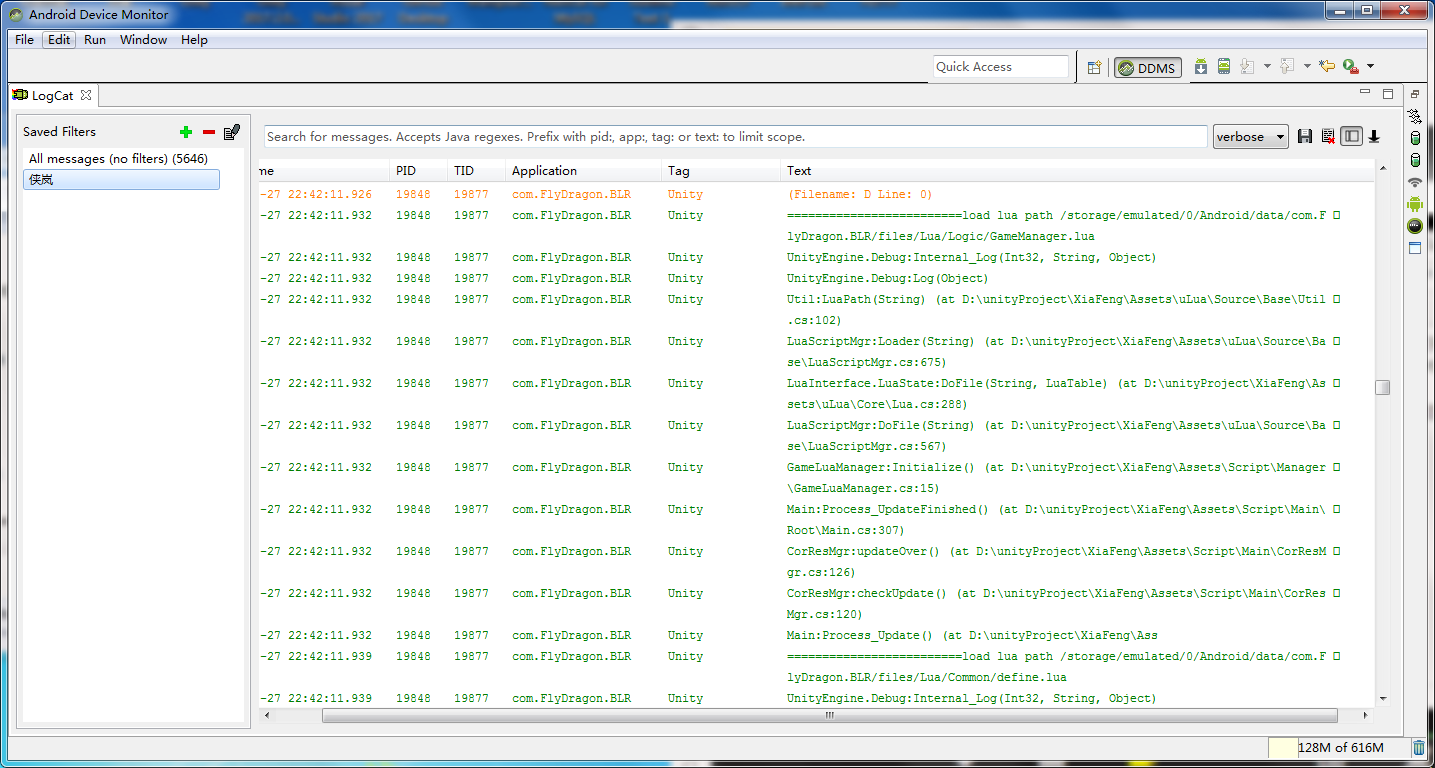
在android-sdk的包中有一个tools工具文件夹,可以双击打开monitor.bat或则是ddms.bat,就会打开一个叫AndroidDeviceMonitor的调试工具,有一个LogCat就是捕捉输出的日志的,他会捕捉android上一切的活动,所以需要新建一个Filter设置Tags为Unity,就可以只看Unity游戏的相关日志了。
在手机上安装好打包后的游戏(开发模式),开启开发者模式的Usb调试,用数据线连接上电脑,然后打开游戏,切换到你游戏的Filter,你就可以看到日志的输出了。
AssetBundle通过Load方法加载资源的时候,是从内存的镜像文件加载成内存的对象,当AssetBundle通过UnLoad(false)卸载资源的时候已经加载出来的资源对象是不会被释放的(只释放镜像内存),需要程序去管理起来了,通过Resource.UnLoad(prefab)卸载掉。
[Test]
[UnityPlatform (RuntimePlatform.WindowsPlayer)]//单个
public void TestMethod1()
{
Assert.AreEqual(Application.platform, RuntimePlatform.WindowsPlayer);
}
[Test]
[UnityPlatform(exclude = new[] { RuntimePlatform.WindowsEditor })]//多个
public void TestMethod2() {
Assert.AreEqual(Application.platform, RuntimePlatform.WindowsEditor);
}UnityPlatform指定在哪些平台才会运行这些测试代码。
[Test]
public void LogAssertExample()
{
//指定一些Log的信息
LogAssert.Expect(LogType.Log, "Log message");
//如果输出的信息不是这一句,就会测试不通过
Debug.Log("Log message");//可以通过
Debug.LogError("Error message");
//如果没有下面这一条,上面这一条就会导致测试不通过了
LogAssert.Expect(LogType.Error, "Error message");
}看注释。
[Test]
public void GameObject_CreatedWithGiven_WillHaveTheName()
{
//一条龙直接往下的
var go = new GameObject("MyGameObject");
Assert.AreEqual("MyGameObject", go.name);
}
[UnityTest]
public IEnumerator TestMono()
{
//需要等待
yield return new MonoBehaviourTest<MonoSSS>();
}
public class MonoSSS : MonoBehaviour,IMonoBehaviourTest
{
public bool IsTestFinished
{
get
{
if (index == 100) return true;
return false;
}
}
int index = 0;
void Update()
{
index++;
}
}Test的测试方法是挺简单的,一般就是将对应需要测试的类实例化一下,然后调用你要测试的方法,最后Assert断言验证数据的正确性。
UnityTest测试的是一个MonoBehaviour的脚本,MonoBehaviourTest返回的是一个IEnumerator,然后等待MonoBehaviour测试的完成。
怎么识别MonoBehaviour脚本测试的完成,就是实现IMonoBehaviourTest接口的IsTestFinished,返回true就表示测试完了。
Test指定的测试,指定是void的方法,就是一条龙往下的测试代码,中间不需要等待的逻辑性代码,例如计算一些数据,工具类转化数据等等。
UnityTest,指定的是返回IEnumertor的方法,就是协程返回,这样就可以用来表示一些加载完资源后测试代码,加载网络消息的测试方法等等可以拥有等待状态。
Unity Test Runner是集成在Unity里面的单元测试,基于NUnit单元测试。使用方法:
在Unity菜单Window->TestRunner打开窗口。
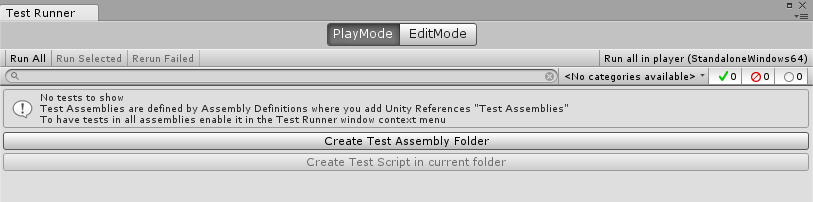
可以看到分为两种模式,一种是PlayMode,一种是EditMode。
PlayMode是一种运行时测试的,就是你运行测试的时候会自动播放游戏的。如果说需要测试MonoBehaviour的脚本,一定得是PlayMode的。
EditMode就是在编辑器当中就可以运行的了,一些普通的脚本啊,一些扩展编辑器的脚本啊等等。
点击Create Test Assembly Folder,创建一个测试的程序集文件夹,会有一个Assembly Definition文件在文件夹里面,可以指定平台。
随后进入到文件夹里面,Create Test Script in current folder就可以用了,点击它,创建一个测试脚本。
using UnityEngine.TestTools;
using NUnit.Framework;
using System.Collections;
public class NewTestScript {
[Test]
public void NewTestScriptSimplePasses() {
// Use the Assert class to test conditions.
}
// A UnityTest behaves like a coroutine in PlayMode
// and allows you to yield null to skip a frame in EditMode
[UnityTest]
public IEnumerator NewTestScriptWithEnumeratorPasses() {
// Use the Assert class to test conditions.
// yield to skip a frame
yield return null;
}
}可以发现使用到了UnityEngine.TestTools和NUnit.Framework。
这里面有两种特性,Test和UnityTest指定的不同的测试方法,在Unity Test Runner中可以看到了

双击就可以测试对应里面的测试代码了。
将这里生成的cs文件和工具箱中的protobuf-net.dll文件一起导入到Unity中,新建一个测试脚本开始序列化和反序列化测试。
using UnityEngine;
using item;
using System.IO;
using ProtoBuf;
public class Test : MonoBehaviour {
void Start () {
Item i = new Item();
i.Type = 1;i.num = 10;i.SubType = 2;
ItemList list = new ItemList();
list.item.Add(i);
byte[] data = Serialize(list);
Debug.LogError(data.Length);//8
ItemList ll = Deserialize<ItemList>(data);
Debug.LogError(ll.item[0].num);//10
}
byte[] Serialize(object o)
{
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
Serializer.Serialize(ms, o);
byte[] result = new byte[ms.Length];
ms.Read(result, 0, result.Length);
return result;
}
}
T Deserialize<T>(byte[] data)
{
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(data))
{
T t = Serializer.Deserialize<T>(ms);
return t;
}
}
}这里使用的Serializer是ProtoBuff命名空间里面的,主要使用它序列化数据在前面加上协议头(就是命令),然后传输过去给服务端,服务端根据协议头找到对应的结构(同一个.proto生成),反序列化(去除)数据
同样的,客户端也是根据服务端的协议头,找到对应的结构,在通过统一接口ProtoBuf反序列化取出数据。
百度搜索"ProtoBuff C#工具",下载编译好的工具集,当然的也可以自己去git上下载源码自己编译。
一、编写.proto文件,就是用来定义数据结构存储什么东西的。
package kongjian;//生成cs文件的命名空间
//import "other.proto";//可以引入其他的定义文件,两个结构其实可以分开两个文件的
message Item
{
required int32 Type = 1;//required表示 必须
optional int32 SubType = 2;//optional表示 可选
required int32 num = 3;
}
message ItemList
{
repeated Item item = 1;//表示数组,解析后为List
}二、利用工具解析为中间文件(.protodesc)再解析为c#类脚本(.cs)
一个工具是protoc.exe,一个是protogen.exe,我的是进入到工具目录中操作的
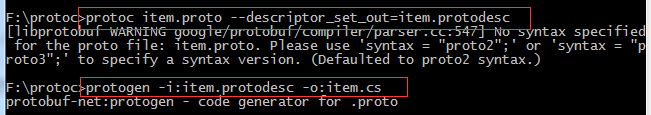
三、看看解析成的cs文件类容
namespace item
{
[global::System.Serializable, global::ProtoBuf.ProtoContract(Name=@"Item")]
public partial class Item : global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible
{
public Item() {}
private int _Type;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(1, IsRequired = true, Name=@"Type", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.TwosComplement)]
public int Type
{
get { return _Type; }
set { _Type = value; }
}
private int _SubType = default(int);
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(2, IsRequired = false, Name=@"SubType", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.TwosComplement)]
[global::System.ComponentModel.DefaultValue(default(int))]
public int SubType
{
get { return _SubType; }
set { _SubType = value; }
}
private int _num;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(3, IsRequired = true, Name=@"num", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.TwosComplement)]
public int num
{
get { return _num; }
set { _num = value; }
}
private global::ProtoBuf.IExtension extensionObject;
global::ProtoBuf.IExtension global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible.GetExtensionObject(bool createIfMissing)
{ return global::ProtoBuf.Extensible.GetExtensionObject(ref extensionObject, createIfMissing); }
}
[global::System.Serializable, global::ProtoBuf.ProtoContract(Name=@"ItemList")]
public partial class ItemList : global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible
{
public ItemList() {}
private readonly global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Item> _item = new global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Item>();
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(1, Name=@"item", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.Default)]
public global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Item> item
{
get { return _item; }
}
private global::ProtoBuf.IExtension extensionObject;
global::ProtoBuf.IExtension global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible.GetExtensionObject(bool createIfMissing)
{ return global::ProtoBuf.Extensible.GetExtensionObject(ref extensionObject, createIfMissing); }
}
}四、同理的,利用同一个.proto文件,可以生成不同平台使用,但是数据结构对应上的客户端文件和服务端文件,这就方便了命令数据结构的对应了。