数据结构和算法
二叉排序树的构建和插入在这里,请先看这个再看查找和删除。
static void Search(Node head,int data,ref Node targetNode, ref Node preNode)
{
//查找方法很简单
targetNode = head;
preNode = null;
while (targetNode != null && targetNode.data != data)
{
preNode = targetNode;
if (data < targetNode.data)
{
targetNode = targetNode.cLeft;
}
else
{
targetNode = targetNode.cRight;
}
}
}
//删除
static void Delete(ref Node head, int data)
{
Node targetNode = null;
Node preNode = null;
Search(head, data, ref targetNode, ref preNode);
if (targetNode == null) return;
if (targetNode.cLeft == null || targetNode.cRight == null)
{
//有一边的结点为空或两边都空,直接删调
Node tempTargetNode;
if (targetNode.cLeft == null)
{
tempTargetNode = targetNode.cRight;
}
else
{
tempTargetNode = targetNode.cLeft;
}
if (preNode == null)
{
head = tempTargetNode;
return;
}
if (preNode.cLeft == targetNode)//左边
{
preNode.cLeft = tempTargetNode;
}
else
{
preNode.cRight = tempTargetNode;
}
}
else
{
//两边都有
//在左边找一个最大的替换,就是目标的前驱。或则找后继,就是右边中最小的
Node LeftBig = targetNode.cLeft;
Node preBig = targetNode;
while (LeftBig.cRight != null)
{
preBig = LeftBig;
LeftBig = LeftBig.cRight;
}
preBig.cLeft = LeftBig.cLeft;//删除替换的节点,对接最大节点的左子树
//对接目标节点的左右子树
if (LeftBig != targetNode.cLeft)//排除特殊情况
{
LeftBig.cLeft = targetNode.cLeft;
}
LeftBig.cRight = targetNode.cRight;
if (preNode == null)
{
head = LeftBig;
return;
}
if (preNode.cLeft == targetNode)//左边
{
preNode.cLeft = LeftBig;
}
else
{
preNode.cRight = LeftBig;
}
}
}删除节点时,需要通过查找得到删除的节点和它的父节点。在删除节点下面的子节点中找一个替换他自己的节点,一个就是前驱一个就是后继了。这里考虑的是前驱。
分两种情况:
一种是,目标节点只有一个或没有子节点没有,只需要将存在的子节点替换掉目标节点就行了,因为但从一边的子树来讲本身就是一个完整的有序的。
另一种是,左右都存在的,直接需要找到前驱了,遍历左子树的右结点,找到最大的节点,移除这个最大的节点,注意这个节点可能存在的左子树要对接上它的父节点。然后将目标节点替换成这个最大的节点,也要注意对接上左右子树。
二叉排序树就是在一棵树中,满足每个结点的左子树结点都比它小,右子树结点比它大。
class Program
{
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node cLeft;
public Node cRight;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] datas = { 9,2,6,3,1,22,8,55,77,33 };
Node head = null;
CreateOrderTree(ref head, datas);
PrintMid(head);//1 2 3 6 8 9 22 33 55 77
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void CreateOrderTree(ref Node head, int[] datas)
{
if (datas.Length < 1) return;
for (int i = 0; i < datas.Length; i++)
{
Insert(ref head, datas[i]);
}
}
//插入
static void Insert(ref Node head, int data)
{
if (head == null)
{
head = new Node();
head.data = data;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
Node preTemp = temp;
bool isLeft = false;
while (temp != null)
{
preTemp = temp;//访问到的最后一个节点,temp是空的
if (data < temp.data)
{
//左边
isLeft = true;
temp = temp.cLeft;
}
else if (data > temp.data)
{
isLeft = false;
temp = temp.cRight;
}
else
{
//重复的数据
return;
}
}
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
if (isLeft)
{
preTemp.cLeft = node;
}
else
{
preTemp.cRight = node;
}
}
//中序遍历输出
static void PrintMid(Node node)
{
if (node == null) return;
PrintMid(node.cLeft);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
PrintMid(node.cRight);
}
}创建一个二叉排序树主要时调用插入方法构建而成的,所以主要的是插入方法,插入方法很简单,都是从树的根开始,每次从根部对比元素,小的往左走,大的往右走,直到为空位置,而这个空的位置就是该元素的位置,所有要保留一个PreNode就是最后访问到的节点和一个左右的标志,好确定新加的元素是最后节点的左还是右子节点。
需要注意的就是树为空的时候,直接跟根赋值就行了。
斐波那契数列是一个:1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34.....,F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)的数列,越往后面,相加的两个数值越接近0.618黄金比例。
斐波那契查找其实和二分法查找很像,只是分割的点不同,二分法除以二得到mid,而斐波那契是通过加减法计算得到mid,运行上会快点吧。
举个例子,对一个有9个元素的数组进行查找,找出接近大于或等于数组大小的斐波那契数列值13。那么我们就可以分成8+5两段,后面元素填充起来。当发现查找的元素在8段,8又可以分成5和3段...
哈弗曼编码是哈夫曼树的一种应用,可以根据习惯统计等,将常用的字母和不常用的字母做成一个权重表。
利用这个权重表构造一颗哈夫曼树,从根节点到每个自己叶节点,每一次要去左结点就是0,每一次去右结点就是1。
这样可以得到每个字母的编码,例如1101,就是从根节点开始,右结点的右结点的左结点的右结点,做一个映射表。
编码的时候,可以通过映射表,将所有的串连成一个 0和1的二进制串,因为常用的被放在了前面,所以很短的二进制编码被用的多次,可以减少二进制串的长度。
解码的时候,遍历二进制串,对应遍历哈夫曼树,0去左,1去右,直到遇到叶节点,输出那个叶节点代表的字母。串继续遍历,哈夫曼树回到根节点从新遍历。
(每一个叶节点的路径都是独一无二的,叶节点之间也没有其他可通路径,所以不会有错码的问题)
带权值的叶节点:就是一个描述这个节点使用频率的系数,越大,表明经常要访问到。
结点路径:从根结点到叶节点要经过的节点数。
树的带权路径长度WPL: 将每个叶节点的权值和它的路径相乘 累加起来的和。
哈夫曼树就是这个WPL值最小的树,要将一颗树改造成哈夫曼树,那么就要将权重值高的放在离根节点相近的地方。
将所有的叶子子节点(子树)从小到大排列
取两个权值最小的子结点,较小的做左孩子,较大的做右孩子,构成一个新的树,根节点为新的,叫他为T吧。
计算T的权值,为两个子节点权值的和,将T放回到1的队伍中,继续2步骤直到队伍只剩下一个根节点了。
线索二叉树就是把一颗二叉树没有使用到的指针利用起来形成的一棵树。
比如说,如果有一个结点的左子节点不存在,我们可以用它指向这个结点的前驱。右结点不存在,就可以指向这个结点的后继。(前驱和后继指的是遍历时的结点顺序,不同的遍历方法不同)
方法就是,在结点中添加两个标志位,一个标志左结点指向的是子节点还是前驱,另外一个标志类似。然后线索化,选择一种遍历顺序(前、中、后序)遍历,为每个结点的空引用赋值前驱或后继,如果前驱或后继为空,那么设置成null。
static void TestAXin()
{
//构造地图
int width = 10;
int height = 10;
Map map = new Map();
map.nodes = new Node[width][];
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
map.nodes[i] = new Node[height];
}
map.XLength = width;
map.YLength = height;
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.X = i;node.Y = j;
if (r.Next(0, 100) > 80)
{
//随机障碍物
node.isOb = true;
}
map.nodes[i][j] = node;
}
}
//寻路
AXin aXin = new AXin();
aXin.SetMap(map);
Console.WriteLine("搜索22到98");
aXin.Search(2, 2, 9, 8);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("搜索85到13");
aXin.Search(8, 5, 1, 3);
}结果:

class Node//结点
{
public bool isOb = false;
public Node Parent;
public int F;
public int G;
public int H;
public int X;
public int Y;
public bool isLine = false;
}
class Map//地图
{
public Node[][] nodes;
public int XLength;
public int YLength;
public void Clear()
{
for (int i = 0; i < XLength; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < YLength; j++)
{
Node node = nodes[i][j];
node.F = 0;
node.G = 0;
node.H = 0;
node.isLine = false;
node.Parent = null;
}
}
}
//输出地图和寻路结果信息
public void PrintMap()
{
for (int i = 0; i < YLength; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
Console.Write(" " + " ");
for (int k = 0; k < XLength; k++)
{
Console.Write(k + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
for (int j = 0; j < XLength; j++)
{
if (j == 0)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Node node = nodes[j][i];
if (node.isLine)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
}
else
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
}
if (node.isOb)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.Write("#" + " ");
}
else
{
Console.Write("*" + " ");
}
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
class AXin//寻找
{
private List<Node> openList;
private List<Node> closeList;
private Map map;
private Node startNode;
private Node endNode;
private Node preNode;
public AXin()
{
openList = new List<Node>();
closeList = new List<Node>();
}
public void Search(int startX, int startY,int endX,int endY)
{
if (map == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("请设置地图");
return;
}
openList.Clear();
closeList.Clear();
map.Clear();
startNode = map.nodes[startX][startY];
if (startNode.isOb)
{
Console.WriteLine("开始位置为障碍物!");
return;
}
endNode = map.nodes[endX][endY];
openList.Add(startNode);
Search();
}
private void Search()
{
bool isSearch = false;
Node tempNode = null;
while (openList.Count > 0 && !isSearch)
{
tempNode = GetLowerFNode();
openList.Remove(tempNode);
closeList.Add(tempNode);
preNode = tempNode; //用来计算其他的结点的F
int x = tempNode.X, y = tempNode.Y;
//遍历周边结点8个 障碍和在close的 忽略
for (int i = -1; i < 2; i++)//x
{
for (int j = -1; j < 2; j++)//y
{
x = tempNode.X + i;
y = tempNode.Y + j;
if (x < 0 || x >= map.XLength || y < 0 || y >= map.YLength)
{
//越界了
continue;
}
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;//中心点
Node node = map.nodes[x][y];
//障碍跳过
if (node.isOb) continue;
//在close里面的跳过
if (isInClose(node)) continue;
//检查对角线 两边有障碍物的不能过
if (i != 0 && j != 0)
{
Node oneNode = map.nodes[tempNode.X][y];
if (oneNode.isOb) continue;
oneNode = map.nodes[x][tempNode.Y];
if (oneNode.isOb) continue;
}
//已经在openList
if (isInOpen(node))
{
//判断是否需要重新算 F
int offsetX = Math.Abs(node.X - preNode.X);
int offsetY = Math.Abs(node.Y - preNode.Y);
int len = 10;
if (offsetX + offsetY == 2)
{
len = 14;
}
if (preNode.G + len < node.G)
{
//重新算
node.G = preNode.G + len;
node.F = node.G + node.H;
node.Parent = preNode;
}
}
else {
//计算F 加进去 设置父物体
CalF(node);
openList.Add(node);
node.Parent = preNode;
if (node == endNode)
{
isSearch = true;
}
}
}
}
}
if (isSearch)
{
Node go = endNode;
//输出结果
while (go != startNode)
{
//Console.WriteLine("X:" + go.X +"||" + "Y:" + go.Y);
//Console.WriteLine("权重F="+go.F +" G="+go.G + " H="+go.H);
go.isLine = true;//标志路径
go = go.Parent;
}
go.isLine = true;
PrintMap();
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("没有找到!");
}
}
public void SetMap(Map m)
{
map = m;
}
//计算F的值
private void CalF(Node node)
{
int offsetX = Math.Abs(node.X - preNode.X);
int offsetY = Math.Abs(node.Y - preNode.Y);
if (offsetX + offsetY == 2)
{
node.G += 14;
}
else {
node.G += 10;
}
//计算方向
int DirectX = Math.Sign(endNode.X - node.X);
int DirectY = Math.Sign(endNode.Y - node.Y);
//计算H的X
int indexX = node.X;
while (indexX != endNode.X)
{
if (map.nodes[indexX][node.Y].isOb == false)
{
node.H += 10;
}
indexX += DirectX;
}
//计算H的Y
int indexY = node.Y;
while (indexY != endNode.Y)
{
if (map.nodes[node.X][indexY].isOb == false)
{
node.H += 10;
}
indexY += DirectY;
}
node.F = node.G + node.H;
}
private bool isInClose(Node node)
{
//可优化 在节点中保存信息
bool isIn = false;
foreach (var i in closeList)
{
if (node == i)
isIn = true;
}
return isIn;
}
private bool isInOpen(Node node)
{
//可优化 在节点中保存信息
bool isIn = false;
foreach (var i in openList)
{
if (node == i)
isIn = true;
}
return isIn;
}
private Node GetLowerFNode()
{
//可优化,用最小堆
if (openList.Count < 1) {
Console.WriteLine("怎么会没有了呢!");
return null;
}
Node node = openList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < openList.Count; i++)
{
if (openList[i].F < node.F)
{
node = openList[i];
}
}
return node;
}
public void PrintMap()
{
map.PrintMap();
}
}首先是将寻路区域分作一个个小方格(我这里是),这是基础
还需要一个评估节点承前启后的消耗,也就是F的计算,G是来到这个节点需要的消耗,H是预计到达目标点的消耗,F是这两个值的和
一个openList记录需要检查周边的节点,closeList记录已经去过的节点(就不用再访问了)
逻辑是这样子的,从openList取出F值最小的加入到closeList中,一开始起点结点会放到openList中
然后遍历这个节点周边的8个节点,障碍物的、在closeList的(访问过的)、斜角边附近有障碍物的都不能通过,直接不做处理;其他的做处理,如果在openList的,要检查当前路径到达这个节点的消耗是否优于以前的,是的话就更换一下F和G值,如果不是,新节点没访问过的,计算一下FGH,加入进去openList。
一直进行下去,直到找到了目标,它要加入到openList,或则openList里面一个元素都没有了。
G - 一个横 一个竖 都是10消耗,一个斜线14消耗(勾股定理)
H - 距离目标横竖偏移和*10(除开障碍物)
F = G + H
char[] dataas = new char[1000000];
for (int t = 0; t < 1000000; t++)
{
if (t == 999999)
{
dataas[t] = '1';
}
else {
dataas[t] = '0';
}
}
char[] searchhs = new char[100];
for (int t = 0; t < 100; t++)
{
if (t == 99)
{
searchhs[t] = '1';
}
else
{
searchhs[t] = '0';
}
}
StringList datas = new StringList(dataas);
StringList search = new StringList(searchhs);
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
int res = datas.Index(search);
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("结果:" + res + " KMP:" + stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
stopwatch.Reset();
stopwatch.Start();
res = datas.SimpleIndex(search);
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("结果:" + res + " Normal:" + stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds);主串是999999个0加个1,匹配串是99个0和一个1,也就是要匹配到最后才能匹配到
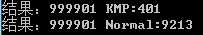 单位ms
单位ms
如果匹配串的0再长点,普通匹配时间会大幅增长。而KMP不会。
KMP的时间复杂度为O(i+j)
//KMP匹配方法
public int Index(StringList T, int pos = 1) {
if (this.isEmpty() || T.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
int mainLength = this.Length();
int matchLength = T.Length();
int i = 1;
int j = 0;
if (pos > 0 && pos <= mainLength) {
i = pos;
int[] nextval = new int[matchLength + 1];
this.getNextval(T, nextval);
for (; i <= mainLength; i++)
{
while (j > 0 && this[i] != T[j + 1])
{
j = nextval[j];
}
if (this[i] == T[j + 1])
{
j++;
}
if (j == matchLength)
{
return i - matchLength + 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}和计算nextvalue数组的方法差不多,就是使用两个指标,主串指标和匹配串指标,将主串指标位置的字符和匹配串指标位置的字符对比,如果相同,就都往后移动一位,如果不相同,匹配串就根据nextvalue的数组回到合适的位置再和主串对比。