数据结构和算法
//出队
public bool DeQueue(ref T element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
Console.WriteLine("队列为空!");
return false;
}
element = this._data[this._front];
//指标向前移动
this._front = (this._front + 1) % (this._maxLength + 1);
return true;
}队头指标向后移,同样需要注意队头指标超过数组下标,需要回到数组开头的情况
//入队
public bool EnQueue(T element) {
if (this.isFull()) {
Console.WriteLine("队列已满!");
return false;
}
this._data[this._rear] = element;
//指标向下移动
this._rear = (this._rear + 1) % (this._maxLength + 1);
return true;
}队尾指标再到达数组最后面的时候,需要从头来过
public bool isEmpty()
{
if (this._rear == this._front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
public bool isFull()
{
int next = (this._rear + 1) % (this._maxLength + 1);
if (next == this._front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}队空的时候很简单,那就是队头和队尾指标等于在一起了
但是队满的情况,队头队尾相等?队尾在队头的下一位?不行
所以,这里留空了一位来判断队满,就是队尾可以在那个留空位上,下一位就一定是队头
因为是循环队列,所以队尾的下一位的表示方式不能简单的+1,要考虑的情况:
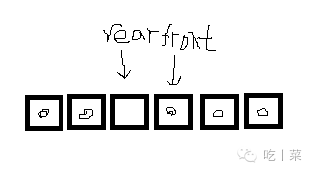
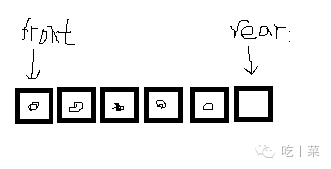
所以用+1再求余的方式来判断是否队满。
队列同样也是一种受限的线性表,是一种先进先出的线性结构。
循环队列是属于顺序存储结构里面很好的实现方式。使用两个指标:队头和头尾指标来构成在数组上的循环使用。这里的队尾指标实际指向的是队尾的下一个元素,作用就是用来判断队列的空满,同时也不影响添加元素。
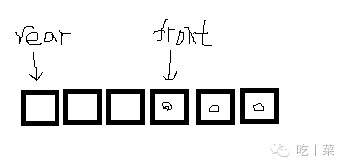
//队列的顺序存储结构-循环队列
class QueueCycleList<T>
{
private T[] _data;
private int _front;
private int _rear;
private int _maxLength = 24;
public QueueCycleList()
{
//留一个空位,用于判断队满的情况
this._data = new T[this._maxLength + 1];
_front = _rear = 0;
}
public QueueCycleList(int length)
{
if (length > 0)
{
this._maxLength = length;
}
this._data = new T[this._maxLength + 1];
this._front = this._rear = 0;
}
}
规则:从左遍历后缀表达式
①如果是数字就入栈
②遇到运算符号,就出栈两个数
③进行运算,先出栈的数在右
public string GoResult() {
int Length = this._laterString.GetListLength();
if (Length <= 0) {
Console.WriteLine("后缀表达式为空!");
return "";
}
string e = "";
//遍历整个后缀表达式
for (int i = 1; i <= Length; i++) {
this._laterString.GetElement(i, ref e);
//如果为符号,出栈两个进行计算
if (e == "+") {
string termElement = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e1 = Double.Parse(termElement);
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e2 = Double.Parse(termElement);
double result = e2 + e1;
this._midStack.Push(result.ToString());
continue;
}
if (e == "-") {
string termElement = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e1 = Double.Parse(termElement);
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e2 = Double.Parse(termElement);
double result = e2 - e1;
this._midStack.Push(result.ToString());
continue;
}
if (e == "*")
{
string termElement = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e1 = Double.Parse(termElement);
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e2 = Double.Parse(termElement);
double result = e2 * e1;
this._midStack.Push(result.ToString());
continue;
}
if (e == "/")
{
string termElement = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e1 = Double.Parse(termElement);
this._midStack.Pop(ref termElement);
double e2 = Double.Parse(termElement);
if (e1 == 0) {
Console.WriteLine("除数不能为0!");
return "";
}
double result = e2 / e1;
this._midStack.Push(result.ToString());
continue;
}
//剩下为数字,入栈
this._midStack.Push(e);
}
//栈中会留有一个元素,那就是结果了
string r = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref r);
return r;
}
规则:从左到右遍历中缀表达式,
①如果是数字就直接输出成为后缀表达式的一部分;
②如果是运算符号,则判断它与栈顶的优先级,如果栈为空或栈顶符号优先级低于等于它或是左括号,就将它入栈,否则输出所有优先级大于等于它的运算符号直到栈空或遇到左括号。
③如果是左括号,直接入栈。
④如果是右括号,匹配到前面的左括号,输出之间的运算符号
//计算出后缀表达式
private bool TranformMidToLater() {
int eleLength = this._elements.GetListLength();
if (eleLength == 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= eleLength; i++)
{
string element = "";
this._elements.GetElement(i, ref element);
if (element == "(")
{
this._midStack.Push(element);
continue;
}
if (element == ")")
{
//匹配前面的左括号
string e = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref e);
while (e != "(")
{
this._laterString.Add(e);
this._midStack.Pop(ref e);
}
continue;
}
if (element == "+" || element == "-")
{
if (this._midStack.GetLength() == 0)
{
//栈中没有元素
this._midStack.Push(element);
continue;
}
//获取栈顶元素
string e = "";
this._midStack.GetTop(ref e);
if (e == "*" || e == "/")
{
//栈顶符号优先级较高,输出
while (e != "(" && this._midStack.GetLength() != 0)
{
this._midStack.Pop(ref e);
this._laterString.Add(e);
this._midStack.GetTop(ref e);
}
}
this._midStack.Push(element);
continue;
}
if (element == "*" || element == "/")
{
this._midStack.Push(element);
continue;
}
//剩下就是数字了
//直接输出
this._laterString.Add(element);
//判断是否为最后一个数字
if (i == eleLength) {
//将中专栈中的符号全部输出
while (this._midStack.GetLength() > 0) {
string e = "";
this._midStack.Pop(ref e);
this._laterString.Add(e);
}
}
}
return true;
}
private bool Match() {
int index = 0;
int exprLength = this._expression.Length;
int lKuo = 0;
int rKuo = 0;
while (index != exprLength) {
char who = this._expression[index];
char next = '\0';
if (index != exprLength-1)
{
next = this._expression[index + 1];
}
switch (who)
{
case '(':
if (index == exprLength - 1 || isRightKuo(next) || isSymbol(next)) {
return false;
}
lKuo++;
//保证前面的左括号多于右括号
if (rKuo >= lKuo) {
return false;
}
this._elements.Add("(");
index++;
break;
case ')':
rKuo++;
if (index == exprLength - 1) {
this._elements.Add(")");
index++;
break;
}
if (index == 0 || isLeftKuo(next) || isNumber(next)) {
return false;
}
if (rKuo > lKuo) {
return false;
}
this._elements.Add(")");
index++;
break;
default:
//如果是符号类型
if (isSymbol(who)){
if (index == 0 || index == exprLength - 1) {
return false;
}
if (isRightKuo(next) || isSymbol(next)) {
return false;
}
this._elements.Add(who.ToString());
index++;
break;
}
if (!isNumber(who)) {
return false;
}
//剩下为数字,匹配数字的范围
int numberLenth = 0;
bool isXiaoShu = false;
while (isNumber(this._expression[index + numberLenth]) || this._expression[index + numberLenth] == '.') {
if (this._expression[index + numberLenth] == '.') {
if (isXiaoShu)
{
//不能有两个小数点以上
return false;
}
else
{
isXiaoShu = true;
}
}
int myIndex = index + numberLenth;
numberLenth++;
if (myIndex == exprLength - 1) {
//最后一个元素
break;
}
}
string num = this._expression.Substring(index, numberLenth);
this._elements.Add(num);
index += numberLenth;
//检查数字的下一个元素
if(index != exprLength)
{
next = this._expression[index];
}
if (isLeftKuo(next)) {
return false;
}
break;
}
}
if (lKuo != rKuo) {
return false;
}
return true;
}向后检查法,只检查当前元素和后面元素的合法性,遍历表达式的每一个元素。
元素类型分为:左括号、右括号,运算符号、数字
左括号,不能是最后一个元素吧。后面不能是右括号和运算符号吧!
右括号,不能是第一个元素吧。后面一定是运算符号吧,其他情况不合格
运算符号,不能是第一和最后一个元素吧。后面不能是运算符号和右括号吧!
数字,后面不能是左括号吧!
匹配元素,主要的就是要把数字匹配出来,只要遇到数字,就一直下一个,直到不是数字为止,注意小数点的出现,只能出现一次,且不是数字的第一位。
普通的我们写出来的2+3运算符号在中间的叫做中缀表达式,通过应用栈转化为后缀表达式,最后通过后缀表达式和应用栈就可以计算出结果了。(博客文章-栈的应用)
class Calculator
{
private string _expression;
public MyList<string> _elements;
private StackList<string> _midStack;
public MyList<string> _laterString;
public Calculator() {
_elements = new MyList<string>(100);
_midStack = new StackList<string>(100);
_laterString = new MyList<string>(100);
}
//计算表达式
public string Cal(string expression) {
this.Clear();//清空那3个线性表
_expression = expression;
if (!this.Match()) {
Console.WriteLine("表达式非法!");
return "";
}
this.TranformMidToLater();
return this.GoResult();
}
}整个计算过程就是:
Match(),匹配计算的元素和检查合法性,例如元素:(、数字、+等;合法性:(后面不能是+号吧?
中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式。
利用后缀表达式计算出结构。
每一个方法的运行,我门认为它是入栈,当一个方法调用完,我们认为它出栈。
递归就是自己方法里面调用自己方法,方法里面提供一个退出点。
//斐波那契数列 递归实现 栈的应用
static int Fbi(int i) {
Console.WriteLine("Fbi(" + i + ") 被调用(入栈)");
if (i < 2)
{
num++;
Console.WriteLine("Fbi(" + i + ") 调用完毕(出栈)");
return i == 0 ? 0 : 1;
}
int a = Fbi(i - 1);
int b = Fbi(i - 2);
Console.WriteLine("Fbi(" + i + ") 调用完毕(出栈)");
return a + b;
}
栈是一种受限的线性表,所以栈的链式存储结构和普通线性表的链式结构差不多。
不同的就是,栈的入栈和出栈(添加和删除)只能在头结点处进行,没有尾结点的概念。